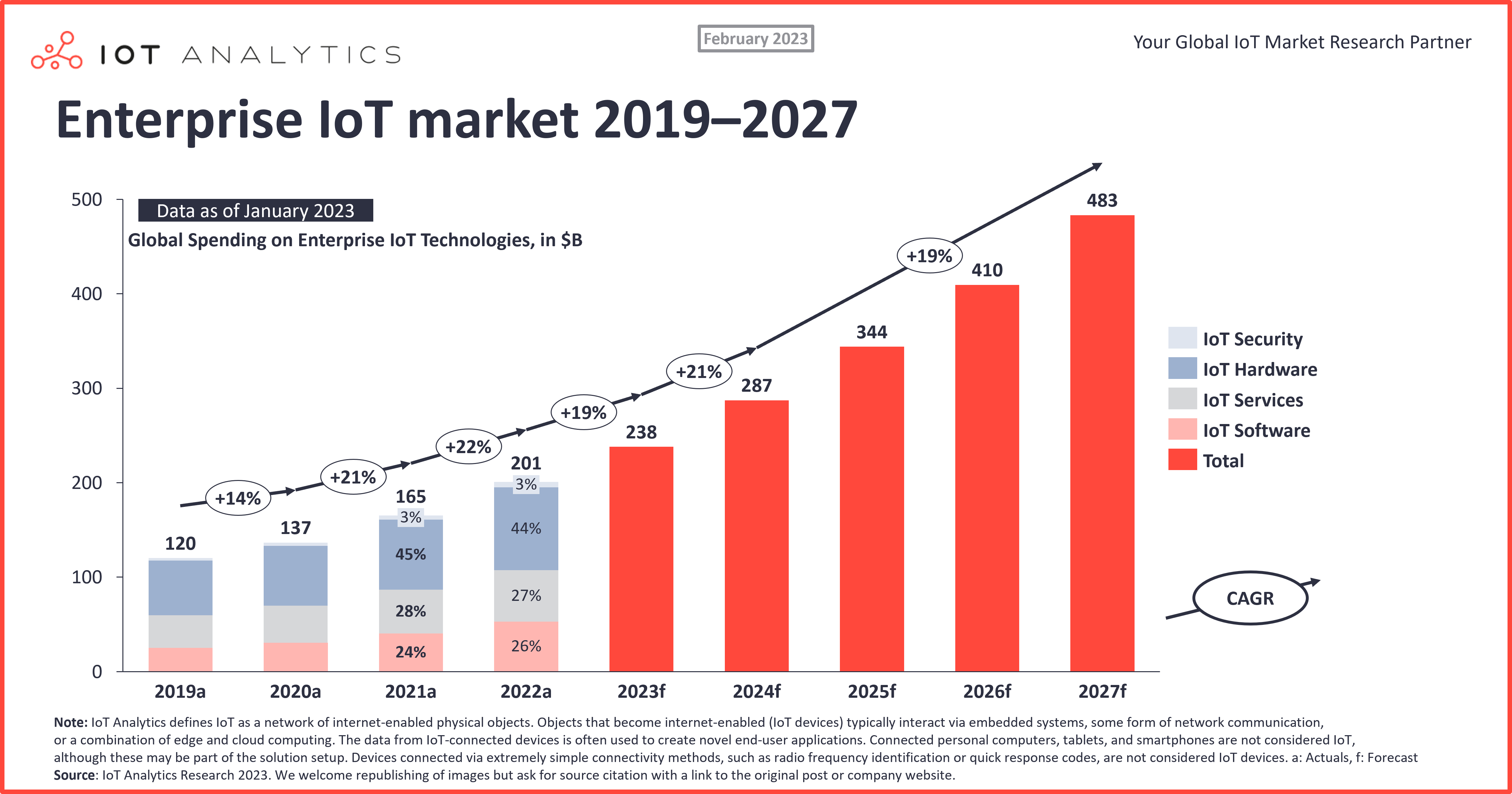
Optimize IoT Core Remote IoT Display Charts With Google Discover!
Can the seemingly simple act of visualizing data revolutionize how we understand and interact with the Internet of Things? The convergence of IoT Core, remote IoT display, and chart representations unlocks unprecedented potential for real-time monitoring, insightful analysis, and proactive control, reshaping industries and transforming everyday experiences.
The evolution of the Internet of Things (IoT) has ushered in an era of unparalleled data generation. From smart homes to industrial automation, connected devices are constantly producing streams of information, painting a dynamic picture of the world around us. However, raw data alone is often overwhelming and difficult to interpret. This is where the synergistic combination of IoT Core, remote IoT display, and chart technologies steps in, transforming complex data into actionable insights. IoT Core serves as the central nervous system, collecting, processing, and securely transmitting data from a myriad of connected devices. Remote IoT displays act as the visual interface, providing users with real-time access to this data, regardless of their physical location. And charts the unsung heroes of data visualization transform raw numbers into easily digestible formats, revealing patterns, trends, and anomalies that would otherwise remain hidden. This trifecta offers a powerful toolkit for making sense of the increasingly complex world of interconnected devices.
Let's consider the core components individually, before considering the synergistic impact of bringing them together. IoT Core, at its essence, is the foundational infrastructure for managing and orchestrating a network of connected devices. It provides the necessary framework for device registration, authentication, secure communication, and data storage. It acts as the intermediary, ensuring that data flows smoothly and securely between the devices and the applications that consume it. The architecture of an IoT Core typically includes:
- Device Management: This module handles the onboarding, configuration, and monitoring of connected devices. It allows for over-the-air updates, remote diagnostics, and device health checks, ensuring the devices function optimally and securely.
- Data Ingestion: This is responsible for receiving data from the connected devices. It handles data formatting, validation, and pre-processing to make it suitable for storage and analysis.
- Security: IoT Core incorporates robust security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. This includes encryption, authentication protocols, and access control mechanisms.
- Data Storage: Data collected from the devices is stored in a scalable and secure manner, often using cloud-based services. This data can be used for real-time monitoring, historical analysis, and machine learning applications.
- Application Integration: IoT Core enables seamless integration with other services and applications, allowing for data to be accessed and utilized for various purposes. This includes integration with data analytics platforms, business intelligence tools, and mobile applications.
The role of a remote IoT display is to extend the reach of this data beyond the confines of a physical location. In essence, it is a digital window into the connected world. These displays can take various forms, from simple dashboards on tablets or smartphones to sophisticated visualizations on large-format screens. They provide users with real-time access to critical information, empowering them to make informed decisions and respond proactively to changing conditions. Key features of effective remote IoT displays include:
- Real-time Data Visualization: The ability to display live data updates, ensuring users have the most up-to-date information at their fingertips.
- Customizable Dashboards: Flexibility to tailor the displayed information to specific needs, allowing users to focus on the most relevant data points.
- Interactive Elements: Features such as drill-down capabilities, filtering options, and alert notifications, enabling users to delve deeper into the data and respond to critical events.
- Secure Access: Robust security measures to protect the displayed data from unauthorized access, ensuring that only authorized users can view and interact with the information.
- Accessibility: Compatibility with a variety of devices and platforms, ensuring the remote display is accessible from anywhere, at any time.
Charts, as the third cornerstone, serve as the linchpin of data interpretation, converting raw data into easily digestible visual representations. The choice of chart type is crucial and depends on the nature of the data and the insights you want to convey. Common chart types include:
- Line Charts: Ideal for visualizing trends over time. They are useful for tracking changes in metrics such as temperature, pressure, or energy consumption.
- Bar Charts: Perfect for comparing values across different categories. They are used to illustrate things like device performance or the distribution of sensor readings.
- Pie Charts: Suitable for illustrating proportions of a whole. They are used when showing the relative contribution of different components or data sets. (though, overuse is sometimes discouraged).
- Scatter Plots: Useful for exploring the relationship between two variables. They are perfect for identifying correlation or patterns in the data.
- Gauge Charts: Offer a visual representation of a single value within a defined range. They are commonly used to illustrate the current status of a sensor reading, such as the temperature of a device.
When these components are combined, the synergistic effect is profound. IoT Core provides the data, the remote IoT display offers the accessibility, and charts bring the data to life. This integrated approach offers numerous benefits across various industries:
- Enhanced Monitoring: Real-time visibility into device performance, enabling proactive issue resolution and reduced downtime.
- Improved Decision-Making: Data-driven insights empower users to make informed decisions, optimizing operations and improving efficiency.
- Increased Efficiency: Automate tasks, optimize resource allocation, and streamline processes.
- Cost Savings: By identifying inefficiencies and preventing failures, the combined solution leads to lower operational costs.
- Enhanced Safety: Early detection of anomalies and potential hazards, leading to improved safety protocols.
Consider the application of this combined solution within a manufacturing environment. IoT Core manages the data streams from various sensors on the factory floor, such as temperature sensors, pressure gauges, and vibration sensors. Remote IoT displays are strategically placed throughout the facility, providing real-time dashboards that show key performance indicators (KPIs) in the form of charts. These charts may display the performance of production lines, the status of machinery, and the overall efficiency of the operations. Management can monitor the entire factory floor from their offices, and technicians can readily identify and address potential issues. This proactive approach reduces downtime, increases productivity, and ensures the smooth running of the manufacturing process. Further, this kind of visibility aids in predictive maintenance; by analyzing the patterns revealed in the charted sensor data, predictive algorithms can be developed to identify which machinery is approaching the end of its service life and needs maintenance.
In the realm of smart agriculture, this combination offers precision farming capabilities. IoT Core collects data from soil sensors, weather stations, and drone imagery. This information is then analyzed and visualized on remote IoT displays, providing farmers with real-time insights into crop health, soil moisture levels, and environmental conditions. Charts display trends in rainfall, temperature, and humidity, allowing farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control. By optimizing these practices, farmers can increase yields, reduce resource consumption, and improve the overall sustainability of their operations. Furthermore, remotely displayed charts can be used to map out the yield and health of various crop plots, aiding in optimized harvesting and field planning. This use of technology has the potential to radically improve food production efficiency.
The application extends into the domain of healthcare. In a hospital setting, IoT Core manages data from patient monitoring devices, such as heart rate monitors, blood pressure sensors, and oxygen saturation sensors. Remote IoT displays, in the form of bedside monitors and central dashboards, provide real-time visibility into patient vital signs. Charts display trends over time, enabling healthcare professionals to quickly identify changes in patient conditions and make timely interventions. This results in improved patient outcomes and a more efficient healthcare delivery system. The remote monitoring capabilities also assist in facilitating faster reaction times in the case of sudden changes in a patients condition. The display of the patient data in chart format assists in easily and quickly understanding any shifts in the patient's health data over time.
In the context of smart cities, the integration of IoT Core, remote IoT displays, and charts can be used to manage a variety of urban services. IoT Core collects data from traffic sensors, environmental monitors, and public safety systems. This data is displayed on dashboards and public displays, providing real-time information on traffic conditions, air quality levels, and crime rates. Charts can illustrate traffic flow patterns, pollution levels, and incident reports, empowering city officials to make informed decisions about resource allocation and public safety strategies. This combination can be leveraged to improve the quality of life for city residents while also optimizing urban infrastructure and efficiency.
While the benefits of combining IoT Core, remote IoT display, and chart technology are evident, there are certain challenges that need to be addressed to ensure successful implementation. These challenges include:
- Data Security: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access and cyber threats. Secure communication protocols, encryption, and access control measures are essential.
- Data Integration: Integrating data from diverse sources and formats can be complex. Standardized data formats and interoperability solutions are important.
- User Experience: Designing user-friendly dashboards and visualizations that are easy to understand and interpret.
- Scalability: Ensuring the system can handle increasing volumes of data and a growing number of connected devices. Scalable architecture and cloud-based services are critical.
- Connectivity: Maintaining reliable and robust network connectivity, especially in remote or challenging environments. Redundancy and failover mechanisms are necessary.
Despite these challenges, the future of IoT Core, remote IoT displays, and chart technology is bright. As the IoT ecosystem continues to grow and evolve, the demand for these integrated solutions will only increase. New innovations, such as the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), will further enhance the capabilities of these systems. For instance, AI algorithms can be used to analyze data, identify patterns, and make predictions. Machine learning can be applied to optimize system performance and automate decision-making processes. In addition, advancements in edge computing will enable data processing to be performed closer to the source, reducing latency and improving responsiveness. This will allow for more complex and real-time insights, resulting in more efficient and proactive applications. The development of intuitive interfaces and user-friendly visualization tools will further expand the accessibility of these solutions, opening up new opportunities across a wide range of industries. The future promises a more interconnected, data-driven, and intelligent world, shaped by the power of IoT, remote displays, and insightful data visualizations.
The success of integrating these three components IoT Core, remote IoT displays, and chart representations hinges on several factors. First, a well-defined strategy is essential. This includes identifying the specific needs and objectives of the application, selecting the appropriate hardware and software, and developing a clear implementation plan. Second, robust data security is paramount. This requires implementing security measures at all levels, from the connected devices to the remote display interfaces. Third, user-friendly design is critical. The dashboards and charts must be intuitive and easy to understand, ensuring that users can quickly extract the information they need. Furthermore, integration with existing systems is vital. This involves ensuring that the IoT solution can seamlessly connect with existing infrastructure, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, business intelligence (BI) tools, and mobile applications. In conclusion, the convergence of these three technologiesIoT Core, remote IoT display, and chartsrepresents a significant leap forward in how we interact with the world of connected devices. By transforming raw data into actionable insights, this integrated approach holds the potential to revolutionize a multitude of industries. As the IoT ecosystem continues to expand and evolve, the ability to visualize and interpret data will be more critical than ever. By understanding the strengths of these technologies and overcoming the challenges of implementation, we can harness their power to create a smarter, more efficient, and more responsive world.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Name of the Technology | IoT Core, Remote IoT Display, Chart Technology |
| Core Functionality | Data Collection, Processing, Visualization and Remote Access |
| Key Components | IoT Core (Device Management, Data Ingestion, Security, Data Storage, Application Integration), Remote IoT Display (Real-time Data Visualization, Customizable Dashboards, Interactive Elements, Secure Access, Accessibility), Charts (Line, Bar, Pie, Scatter, Gauge) |
| Application Areas | Manufacturing, Smart Agriculture, Healthcare, Smart Cities |
| Benefits | Enhanced Monitoring, Improved Decision-Making, Increased Efficiency, Cost Savings, Enhanced Safety |
| Challenges | Data Security, Data Integration, User Experience, Scalability, Connectivity |
| Future Trends | AI/ML Integration, Edge Computing, Improved User Interfaces |
| Related Technologies | Cloud Computing, Data Analytics, Big Data, Machine Learning, Edge Computing, AI |
| Link to Reference | Example IoT Reference (Replace with an actual, relevant URL) |