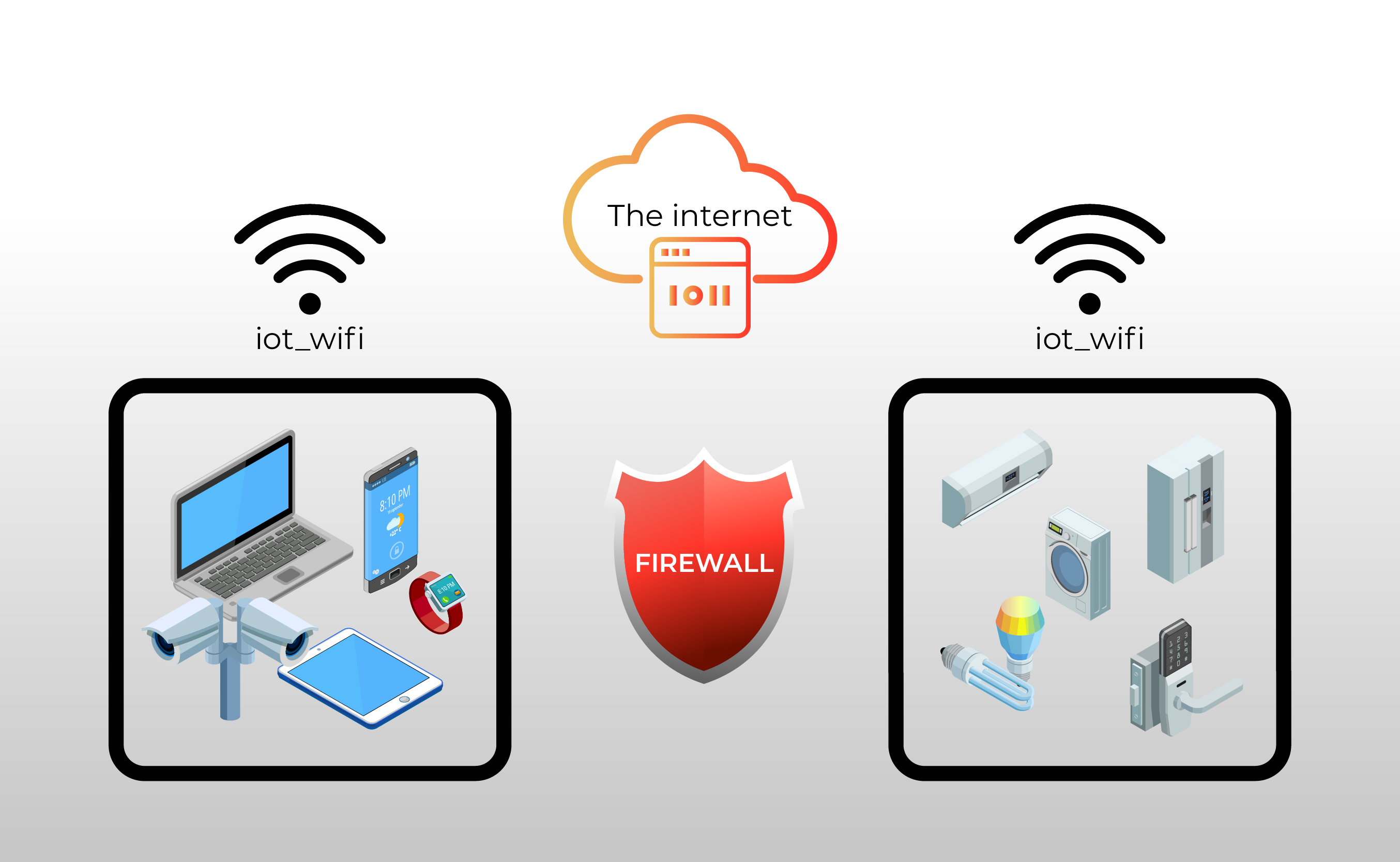
Secure Remote IoT Access: Behind The Firewall & Beyond
Is the promise of the Internet of Things (IoT) being stifled by the very barriers it's designed to transcend? The reality is stark: deploying and managing IoT devices securely behind firewalls presents a complex challenge, but one that must be overcome to unlock the true potential of a connected world.
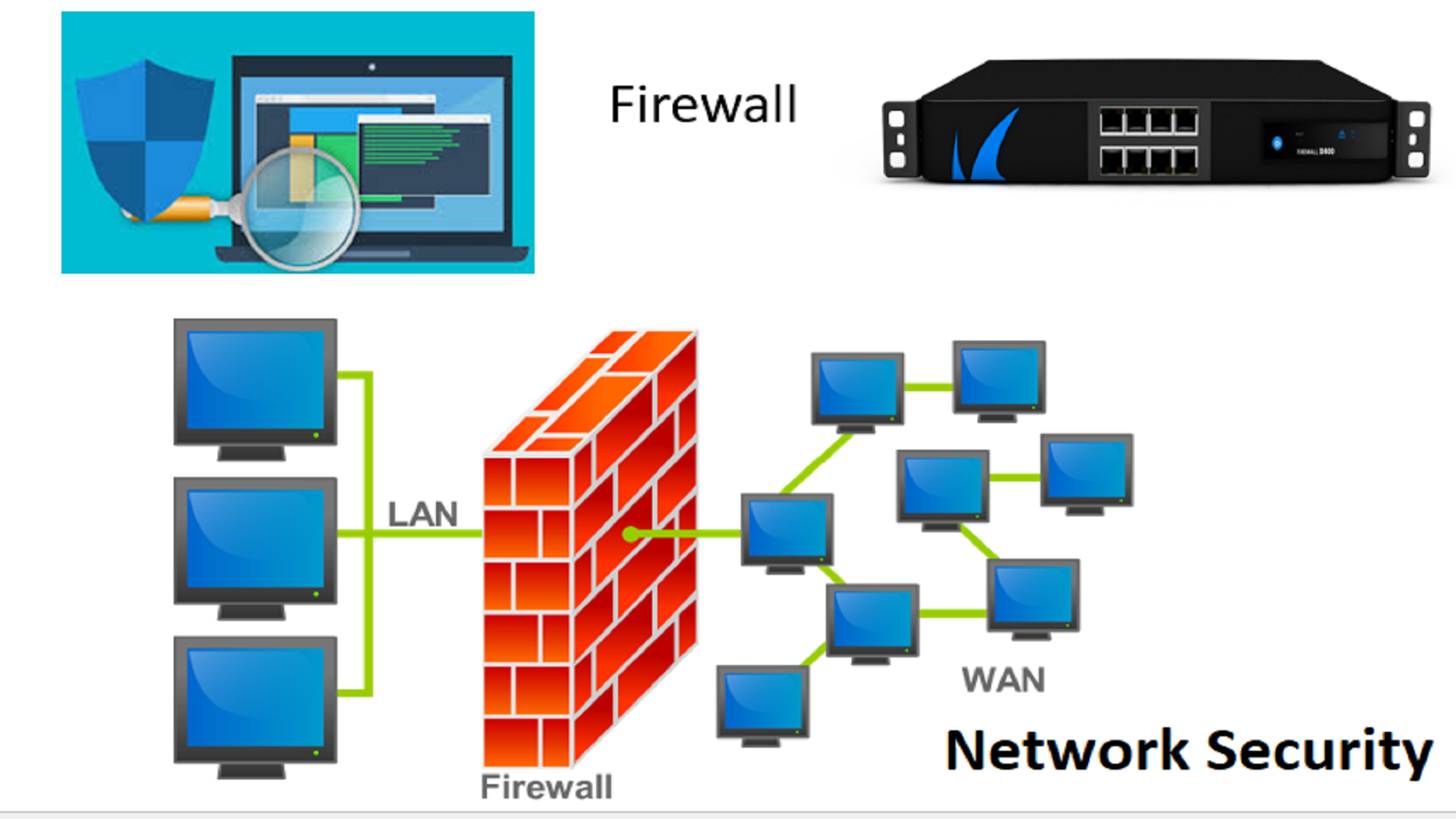
The explosion of connected devices, from industrial sensors to smart home appliances, has created a landscape brimming with possibilities. Yet, the inherent security risks associated with these devices, coupled with the stringent security measures often mandated by organizations, have created a significant hurdle. The firewall, the cornerstone of network security, designed to protect sensitive internal systems, now finds itself acting as a gatekeeper, potentially hindering the seamless flow of data and commands essential for effective IoT deployments. The challenge lies in finding a balance: enabling the benefits of IoT while maintaining robust security protocols.
The issue of "remoteiot behind firewall" encapsulates this tension perfectly. It highlights the difficulty of securely connecting and managing IoT devices that reside within a protected network perimeter. This isn't merely a technical problem; it's a strategic one. Organizations must navigate the complexities of network configurations, data encryption, and access control to ensure that IoT deployments are not only functional but also resilient against cyber threats. The solutions, therefore, require a multi-faceted approach, combining technological innovation with a deep understanding of risk management.
The concept of IoT, in its essence, is about extending the reach of the internet to physical objects. These objects, whether they are embedded in manufacturing equipment, monitoring environmental conditions, or managing energy consumption, are designed to collect, process, and transmit data. This data, often containing valuable insights, needs to be securely accessed and utilized. But the traditional approach of opening up firewall ports to allow external access to these devices is a dangerous proposition, exposing internal networks to potential breaches. The challenge is therefore to permit the free flow of data from the connected devices to the central systems, while simultaneously implementing security measures that prevent unauthorized access and malicious attacks.
Consider the manufacturing sector, where IoT is revolutionizing production processes. Sensors embedded in machinery provide real-time data on performance, allowing for predictive maintenance, optimized resource allocation, and increased efficiency. However, these sensors are typically deployed behind firewalls to protect sensitive manufacturing data and intellectual property. Managing these devices remotely, deploying updates, and extracting data necessitates secure methods of communication that circumvent the inherent restrictions of the firewall. The same principles apply to other sectors, such as healthcare, where medical devices and patient monitoring systems require secure access and data transfer, while rigorously adhering to privacy regulations.
The strategies for successfully implementing "remoteiot behind firewall" are varied and evolving. One common approach involves the use of secure tunnels, such as virtual private networks (VPNs) or secure shell (SSH) connections, which create encrypted pathways for communication between devices and central servers. These tunnels provide a secure conduit, allowing data to traverse the firewall without exposing the internal network to direct external access. However, the setup and maintenance of VPNs can be complex, especially in environments with numerous devices and dynamic IP addresses. Furthermore, the reliance on VPNs can introduce latency, which may impact the real-time performance of IoT applications.
Another approach involves the use of IoT-specific platforms and gateways. These platforms provide a centralized point of management for connected devices, offering features such as device provisioning, secure authentication, and over-the-air (OTA) updates. IoT gateways act as intermediaries, translating protocols, aggregating data, and providing a secure channel for communication. They often employ advanced security features like encryption, device identity management, and intrusion detection systems, adding an extra layer of protection. These platforms can also facilitate communication through firewalls by utilizing specific protocols that are allowed by default, such as HTTPS or MQTT over TLS.
The choice of solution will inevitably depend on the specific requirements of each deployment. Factors to consider include the number and type of devices, the sensitivity of the data, the existing network infrastructure, and the organization's security policies. A thorough risk assessment is crucial, identifying potential vulnerabilities and determining the appropriate security measures to mitigate those risks. This assessment should include considerations for device authentication, data encryption, access control, and ongoing monitoring.
The concept of zero trust networking is gaining traction in this context. This model assumes that no user or device, whether inside or outside the network perimeter, is inherently trustworthy. Instead, every access request is verified, and devices are constantly monitored for suspicious activity. In the context of "remoteiot behind firewall," this approach can strengthen security by limiting the attack surface and ensuring that only authorized devices can access sensitive data. Zero trust frameworks typically incorporate multifactor authentication (MFA), micro-segmentation, and continuous monitoring to provide a more robust security posture.
The rise of edge computing also has a significant impact on the "remoteiot behind firewall" challenge. Edge computing involves processing data closer to the source, on the IoT device itself or on a nearby gateway. This can reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted across the firewall, which in turn can reduce the attack surface and improve performance. Furthermore, edge computing can facilitate real-time decision-making, enabling quicker responses to events and improved operational efficiency. However, even with edge computing, the need for secure communication and management of devices behind the firewall remains critical.
Implementing effective "remoteiot behind firewall" solutions also requires attention to device lifecycle management. This involves a comprehensive approach to managing devices from deployment through decommissioning. It requires secure provisioning, over-the-air updates, and regular vulnerability assessments. Furthermore, secure decommissioning is just as important as secure deployment, ensuring that devices are properly wiped and that any sensitive data is securely erased. Proper device lifecycle management minimizes the risk of compromised devices and data breaches.
Another aspect is the importance of choosing the right communication protocols. Many IoT devices use protocols like MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP. Secure versions of these protocols, such as MQTT over TLS/SSL and HTTPS, should be used whenever possible. These protocols provide encryption and authentication, ensuring that data is protected during transit. The choice of protocol will also depend on factors such as bandwidth constraints, latency requirements, and device capabilities. Furthermore, network administrators need to understand the security implications of each protocol and configure them properly to mitigate vulnerabilities.
The role of cloud platforms in "remoteiot behind firewall" solutions is significant. Cloud-based IoT platforms often provide the necessary infrastructure, tools, and services for managing connected devices, including secure communication channels, device management capabilities, and data analytics tools. These platforms offer scalable and cost-effective solutions that simplify the complexities of IoT deployments. However, organizations must also carefully consider the security and privacy implications of storing data in the cloud and ensure that the chosen cloud provider adheres to relevant compliance standards.
The regulatory landscape also shapes the approach to "remoteiot behind firewall." Organizations must comply with various regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, which govern the collection, processing, and storage of personal data. These regulations place stringent requirements on data security and privacy, which directly impact the design and implementation of "remoteiot behind firewall" solutions. Compliance requires a comprehensive understanding of the regulations and the implementation of appropriate security measures to protect sensitive data. It necessitates ongoing monitoring and audits to ensure continued compliance.
Training and awareness are essential components of a successful "remoteiot behind firewall" strategy. Its crucial for organizations to provide comprehensive training to their IT staff and other personnel on IoT security best practices. This training should cover topics such as device security, network security, data encryption, and threat detection. Awareness programs should also be implemented to educate employees about the risks associated with IoT devices and the importance of following security policies. Regular training and awareness programs are essential to maintain a strong security posture and minimize the risk of human error.
The future of "remoteiot behind firewall" is likely to involve a combination of advanced technologies and strategies. The increasing adoption of 5G networks will provide faster and more reliable connectivity for IoT devices, which will necessitate more sophisticated security measures. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will also play an increasingly important role, automating threat detection, analyzing security logs, and predicting potential vulnerabilities. The focus will be on creating more resilient and adaptable security solutions that can effectively protect IoT deployments in a rapidly evolving threat landscape.
In conclusion, successfully implementing "remoteiot behind firewall" solutions is crucial for organizations seeking to harness the power of IoT. It requires a comprehensive approach that combines robust security measures with a deep understanding of the challenges. Organizations must carefully assess their risks, choose the appropriate technologies and protocols, and implement rigorous security policies and training programs. By adopting a proactive and adaptive security strategy, organizations can unlock the full potential of IoT while protecting their networks from potential threats. The challenge is not simply about enabling connectivity; it's about doing so securely and reliably, paving the way for innovation and progress in a connected world.
The journey to achieve this requires constant vigilance and a willingness to embrace new technologies and strategies. The rewards, however, are substantial: increased efficiency, improved decision-making, and a competitive edge in an increasingly connected world. The organizations that prioritize "remoteiot behind firewall" will be the ones that thrive in the age of IoT.